engineering & technology publications
ISSN 1759-3433
PROCEEDINGS OF THE SEVENTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURES TECHNOLOGY
Correlation Coefficients of Modal Oscillators with Viscoelastic Memory
Department of Construction and Advanced Technology, University of Messina, Italy
In the design practice, nevertheless, rigorous analyses are avoided, and simplified assumptions are usually considered. In particular, the classical mode superposition technique, in conjunction with a given spectrum, can be applied, but modal shapes, modal frequencies and modal damping ratios are to be computed by means of the Modal Strain Energy (MSE) method. It has been shown [2] that the arising error is smaller for proportionally damped structures, i.e. with decoupled modal oscillators. Even if not rigorous, this assumption is frequently met in real structures, since the distribution of the viscoelastic dampers is almost homogenous in the primary structure. On the contrary, the definition of an equivalent viscous dissipation for the modal oscillators may lead to some degrees of inaccuracy [3]. First, the fading memory introduced in the primary structure together with the viscoelastic dampers is totally neglected: in so doing, depending on the dynamic characteristics of the input and of the composite system, the response of the modal oscillators may be largely under- or over-estimated. Furthermore, when the classical Complete Quadratic Combination (CQC) rule is applied, the use of the correlation coefficients available in the literature is not boundless: these coefficients, in fact, have been derived under the assumption of a linear viscous damping, but this approximation may be unrealistic in presence of a non-negligible viscoelastic memory.
In the present study, alternative procedures to consistently evaluate the correlation coefficients of modal oscillators with viscoelastic memory are proposed. Firstly, a direct approach in the frequency domain is considered, which can be used with any coloured input. The main disadvantage is that some integrals have to be numerically computed. Then, a time-domain approach is proposed in the simplest case of white noise input, in which the correlation coefficients are directly obtained from linear equations, made compact with the Kronecker algebra [4]. Finally, this approach is extended to the more realistic case of filtered white noise, in which the correlation coefficients are obtained by solving in cascade more linear equations.
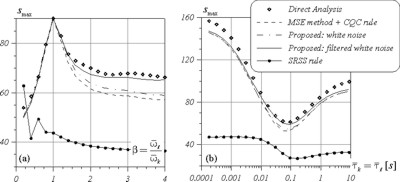
Monte Carlo simulations are used to validate the proposed approaches. The numerical examples demonstrate that the inaccuracy of the conventional MSE method, used together with the classical CQC rule, may be unacceptable for engineering purposes. On the contrary, the proposed formulations always improve the results, as it is shown in Figure 1 for rigid soil.
- 1
- A. Palmeri, F. Ricciardelli, A. De Luca, G. Muscolino, "State space formulation for linear viscoelastic dynamic systems with memory," J. of Engineering Mechanics - ASCE, 129, 715-724, 2003. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2003)129:7(715)
- 2
- A. Zambrano, J.A. Inaudi, J.M. Kelly, "Modal coupling and accuracy of Modal Strain Energy method," J. of Engineering Mechanics - ASCE, 122, 603-612, 1996. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1996)122:7(603)
- 3
- A. Palmeri, F. Ricciardelli, G. Muscolino, A. De Luca, "Effects of viscoelastic memory on the buffeting response of tall buildings," Wind and Structures, 7, 89-106, 2004.
- 4
- A. Graham, "Kronecker Products and Matrix Calculus with Applications", Ellis Horwood, Chichester, 1981.
purchase the full-text of this paper (price £20)
go to the previous paper
go to the next paper
return to the table of contents
return to the book description
purchase this book (price £135 +P&P)