Computational & Technology Resources
an online resource for computational,
engineering & technology publications
engineering & technology publications
Civil-Comp Proceedings
ISSN 1759-3433
ISSN 1759-3433
CCP: 79
PROCEEDINGS OF THE SEVENTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURES TECHNOLOGY
PROCEEDINGS OF THE SEVENTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURES TECHNOLOGY
Edited by: B.H.V. Topping and C.A. Mota Soares
Paper 109
Dynamic Elastic Analysis of MDOF Structures with Random Strengths
S. Benfratello and F. Giambanco
Department of Structural and Geotechnical Engineering, Universita' degli Studi di Palermo, Italy
Full Bibliographic Reference for this paper
S. Benfratello, F. Giambanco, "Dynamic Elastic Analysis of MDOF Structures with Random Strengths", in B.H.V. Topping, C.A. Mota Soares, (Editors), "Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Computational Structures Technology", Civil-Comp Press, Stirlingshire, UK, Paper 109, 2004. doi:10.4203/ccp.79.109
Keywords: uncertainties, probabilistic analysis, dynamic analysis, elastic analysis.
Summary
The numerical values of the constants appearing in constitutive laws show a
random behaviour and the international standard ENV 13005 [1] established the criteria
for the probabilistic characterization of such values. The structural response must be
therefore considered as random variable whose characteristics have to be
appropriately determined. In the framework of structural analysis a fundamental role is
played by elastic limit analysis which provides the maximum load multiplier such
that the structure remains everywhere in elastic field. Many important actions on
structures such as wind, wave and earthquake, possess a strongly dynamic behaviour
and the appropriate tools for structural dynamic analysis have to be adopted. Further,
stress levels in the structure during transient phase can be much greater than the
corresponding ones in stationary phase and therefore appropriate tools for performing
limit analysis in the case of dynamic actions are of great interest. In the paper the
dynamic elastic limit analysis of MDOF discrete or discretised structures subjected
to analytical forcing function (i.e. unit step function or sinusoidal function) by
assuming the yield stress of material as random variable, whose characteristics are
known, is performed. In the paper the exact probability density function of the limit
elastic load multiplier is determined as that of the minimum of random variables
obtained as a linear transformation of the random yield stresses. The 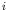 -th limit elastic
multiplier is given as
-th limit elastic
multiplier is given as
being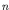 the number of degrees of freedom of the structure,
the number of degrees of freedom of the structure,
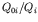 are the
are the 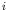 -th
element of the vectors
-th
element of the vectors
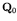 (yield stress vector) and
(yield stress vector) and
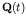 (actual stress vector),
respectively. In matrix form equation (43) can be written as follows
(actual stress vector),
respectively. In matrix form equation (43) can be written as follows
As it can be easily seen, the coefficients of transformation (44) are time dependent. The exact probability density function of the limit elastic load multiplier is given by
being
As it can be easily seen, the coefficients of transformation (44) are time dependent. The exact probability density function of the limit elastic load multiplier is given by
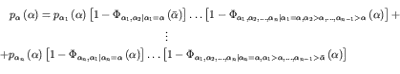 |
(45) |
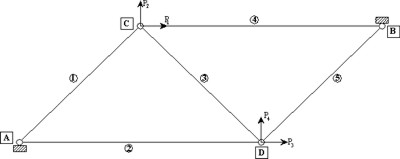
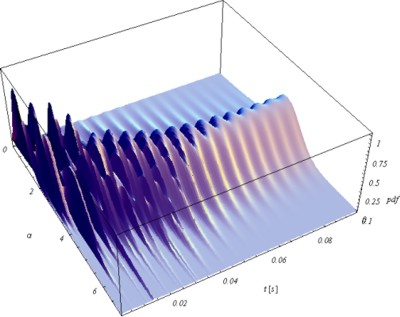
Since the computational effort required by equation (45) can be very high a very simple approximated formula is also presented. This approximated formula represents an upper bound of the exact one and it is obtained from equation (45) simply by assuming the random variable as independent. Numerical application to the truss sketched in figure 1 confirms that the proposed approach allows to easily take into account the role played by the transient phase. In figure 2 the probability density function of the limit elastic multiplier is reported.
References
- 1
- UNI CEI ENV 13005:2000, Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement.
purchase the full-text of this paper (price £20)
go to the previous paper
go to the next paper
return to the table of contents
return to the book description
purchase this book (price £135 +P&P)